Sarcoidosis is a rare inflammatory condition that develops when a group of cells in the immune system form patches of swollen tissue. These are called granulomas.
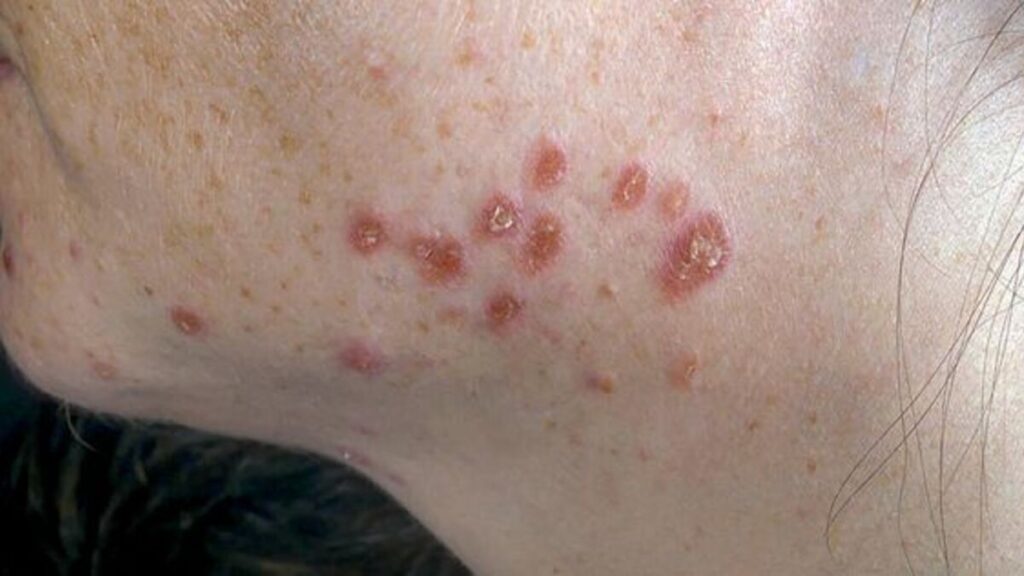
While most people see an improvement in a few months or years, sarcoidosis can also be a life-threatening illness. Therefore, it is essential to know this disease’s symptoms and risk factors.
What Is Sarcoidosis?
Sarcoidosis is a rare disease that develops when groups of immune cells form small patches of tissue in the body’s organs. It is uncommon and affects about 1.2 million people around the world.
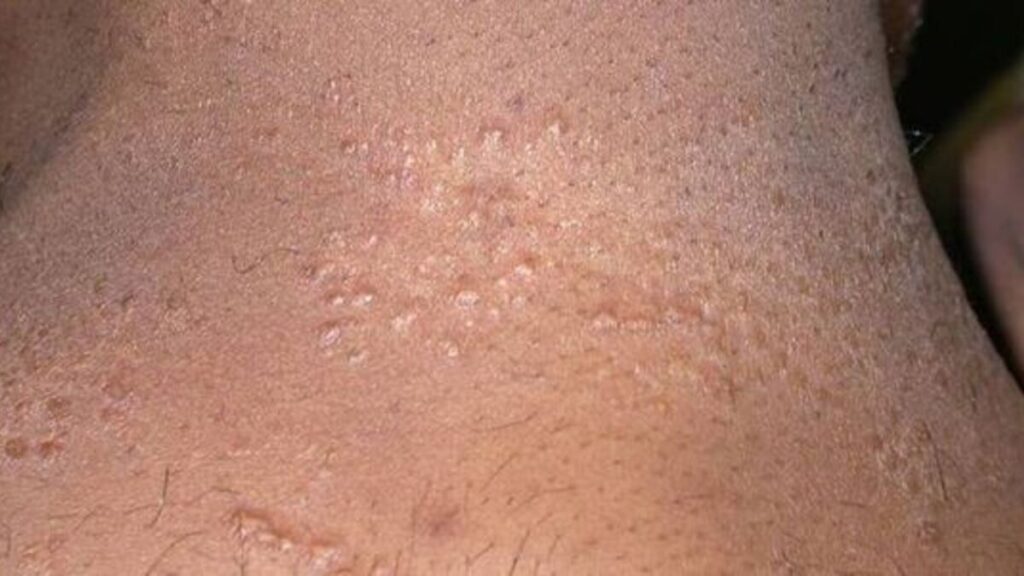
Furthermore, it can affect many body parts, including the eyes, skin, lungs, heart, and nervous system.
Causes of Sarcoidosis
The disease usually develops as an autoimmune response by the body. While there is no direct cause, experts have traced its genetic origin. It could also have an environmental component that can cause the immune system to go into overdrive.
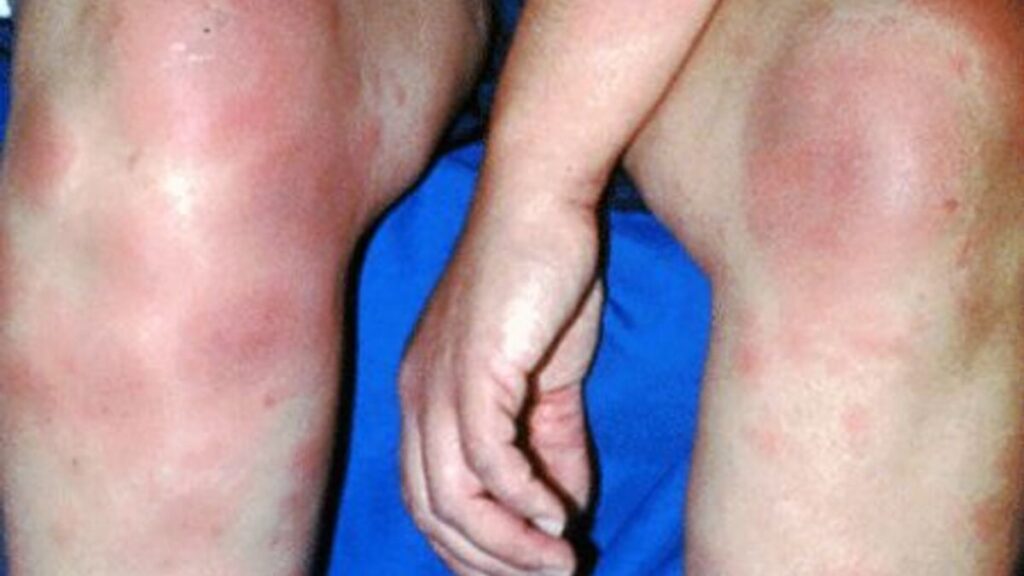
It usually starts in the lungs or lymph nodes and then shows signs and symptoms around the body.
Symptoms of Sarcoidosis
The symptoms of this condition vary widely depending on the severity and organs of affectation. For example, those whose lungs are affected have symptoms consistent with lung damage.
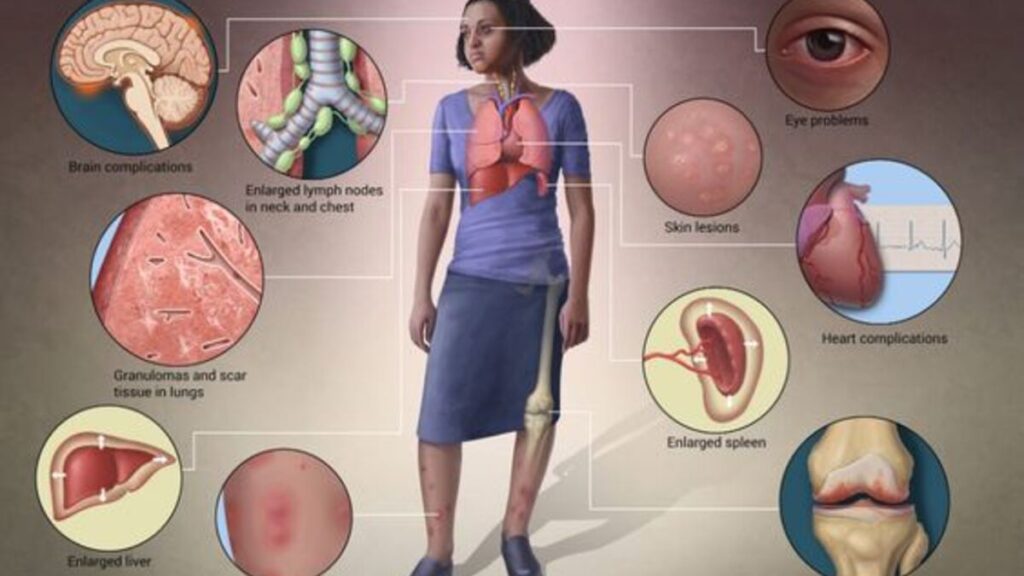
It could also affect the kidneys, heart, and skin, causing symptoms like tachycardia, erythema, and severe fever. These are usually why people go to the hospital to know what’s wrong with them.
ALSO READ: Wolves Thrive in Chernobyl’s Radioactive Land, Develop Unexpected Abilities
Skin Symptoms of Sarcoidosis
More often than not, sarcoidosis affects the skin. This is a primary symptom of the disease. This is called Lofgren syndrome.
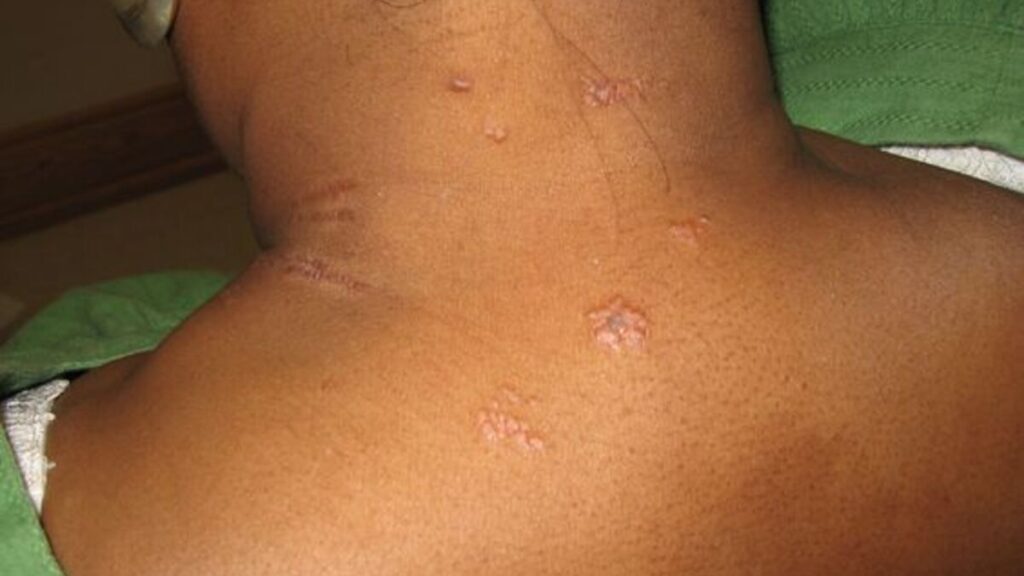
It is a classic triad of fever, erythema nodosum, and bilateral hilar adenopathy (enlargement of the pulmonary lymph nodes). In addition, swollen and painful joints around the body cause discomfort. Red, raised, and tender bumps are also common.
Pulmonary Symptoms
When sarcoidosis strikes the lungs, it is often quite severe. Therefore, the patient experiences wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Those who present with pulmonary symptoms are classified as having pulmonary sarcoidosis. In severe cases, the lungs become inflamed, which eventually results in fibrosis. Therefore, it is important to treat it as soon as possible.
POLL — Should Donald J. Trump Be Allowed to Run for Office?
Cardiac and Renal Symptoms
Sarcoidosis can affect the heart and kidneys at various stages. Therefore, it is important to monitor the function of these organs, as they can increase the severity.
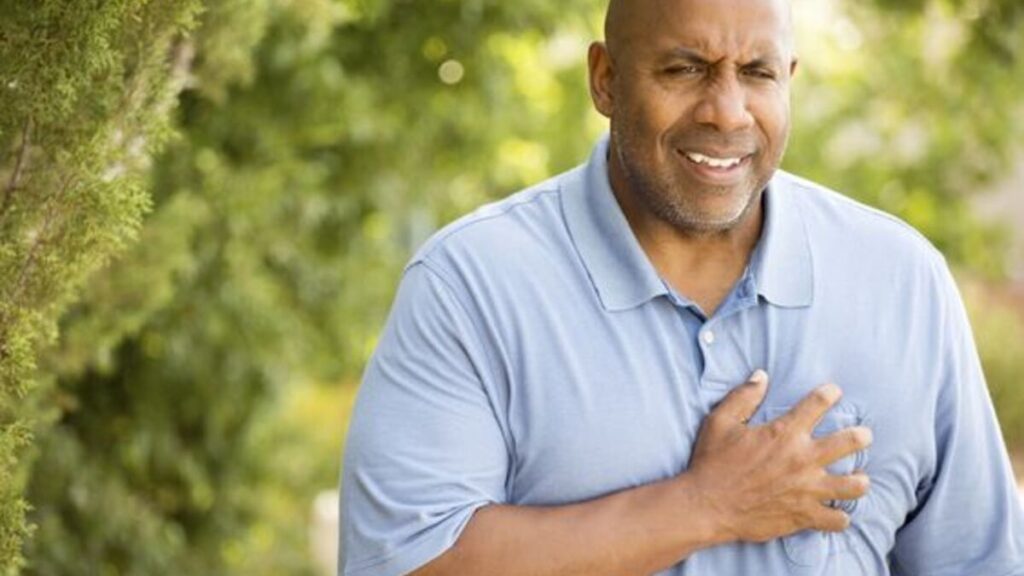

Cardiac sarcoidosis can cause arrhythmia and even death through heart failure. On the other hand, renal sarcoidosis usually presents with high calcium levels in the blood, causing kidney stones.
Risk Factors
As mentioned earlier, sarcoidosis has varying risk factors. These include advanced age, environmental issues, work factors, family history, genetics, race, and ethnicity.

Therefore, people with a higher risk factor need to be careful about developing the disease. While the severity can be different, it is best to never have it at all. Some risk factors are beyond one’s control, but you can monitor others.
ALSO READ: “I Didn’t Pay Attention,” Christina Applegate Recounts MS Symptoms
Environmental Issues and Working Conditions
One’s place of residence is a considerable risk factor for the disease. For those who live in places infested with mold, pollutants, or other substances, this may cause constant inflammatory reactions in the body.
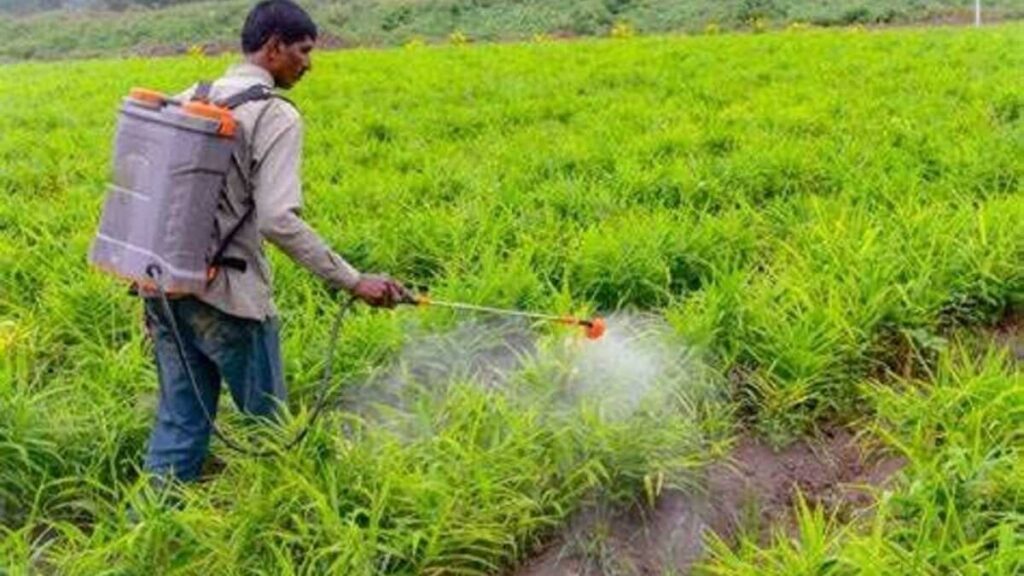

Furthermore, people who work in places like factories with insecticides are prone to lung infections, which can trigger inflammation and lead to sarcoidosis.
Age
Age is a considerable risk factor for sarcoidosis. As most people know, an increase in age means an increase in disease susceptibility, so older people are prone to this disease.

Most significantly, those over the age of 55 have a higher chance of developing the disease. In addition, it may be more difficult to treat older people with this condition.
Family History, Genetics, Race and Ethnicity
People with family members who have sarcoidosis have a higher chance of developing this condition. This is because scientists have found a genetic link that can cause people from a particular bloodline to be more susceptible.
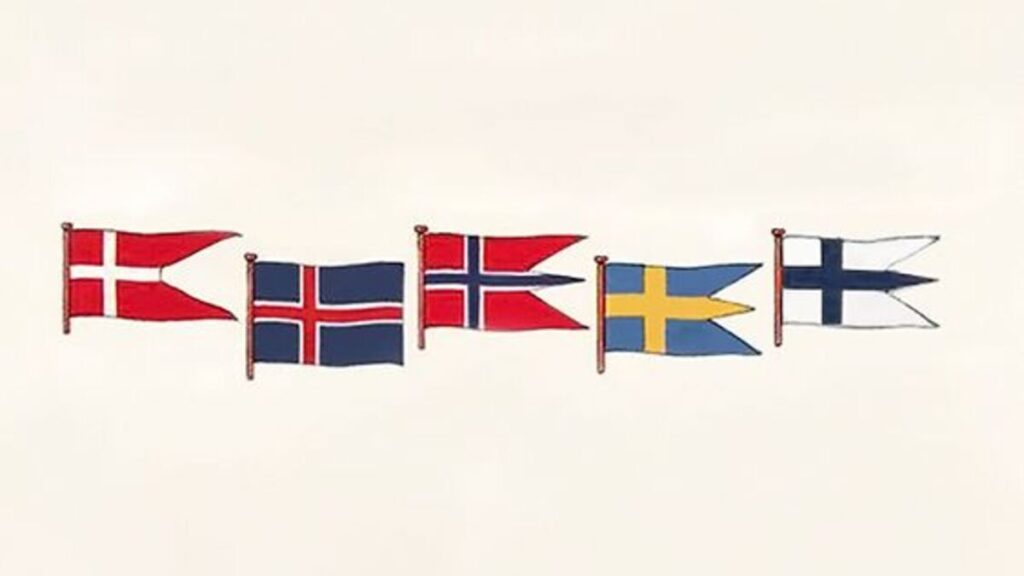

Race, ethnicity, and descent can also play a huge role. For example, Scandinavian people have a higher chance than black people.
ALSO READ: Health Officials Demand Urgent Action as U.S. Faces Growing Disease Threats
Diagnosis and Treatment
Those who suspect sarcoidosis need to go to the hospital for treatment. Doctors will run several tests, including a CT scan, lung function test, and blood test, to confirm the presence of the condition.

Most people with sarcoidosis do not require treatment. The condition usually disappears on its own after a few months or years. However, doctors typically prescribe corticosteroids as a primary form of therapy.
Life Expectancy and Prognosis of Sarcoidosis
Most of the time, the condition is not life-threatening. Therefore, with proper management and medical care, there is a meager chance of death or severe damage.
Symptoms also improve with time as the body tries to heal itself. About 60% of granulomas that cause sarcoidosis cases will disappear over two to five years, and the patient will recover. Relapse is also unlikely.
You Might Also Like:
Florida Restaurant Set To Appear in Brad Pitt’s Film Goes Up in Flames
Black Men Tortured, Wrongly Charged by Mississippi Officers Call for “Stiffest of Sentences”
Legal Experts Say Mike Lindell’s New Supreme Court Evidence Is Bound to Fail
Chicago Enforces Controversial Policy, Evicts Migrants From Shelters
Biden Suffers Blow As Supreme Court Allows Texas To Arrest Illegal Migrants From the Southern
